A Natural Treatment for Lung Cancer?
You won’t find it on the shelf of your local garden center but the natural plant extract called deguelin, used as an insecticide in Africa and South America, appears to prevent the growth of precancerous and cancerous lung cells without harming normal cells. The findings, published in the February 2003 issue of the US Journal of the National Cancer Institute, suggest a possible nontoxic treatment for lung cancer.
The compound belongs to the same family as other healing-enhancing plant compounds called flavonoids, found in tea, coffee and red wine. It appears to work by affecting a molecule called Akt, which is responsible for the survival of tumor cells. By blocking the cells’ ability to send out survival signals, the compound causes them to commit 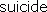 . .
“The results of our study provide evidence for the first time that Akt is essential in the growth of precancerous human bronchial epithelial cell line, and that deguelin can be a potential chemopreventive agent against lung cancer,” according to Ho-Young Lee, Ph.D., lead investigator of the study, which was conducted by researchers at UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Several studies have shown that Akt provides a critical cell survival signal for tumor progression by adding phosphate to the proteins involved in cell cycle regulation and pre-cell death factors. Results of this study found that the activation of Akt is a common feature in the early stages of cancer and that inhibition of Akt might be a potential target for chemoprevention. Deguelin is an optimal agent for this goal, according to the results of the study, as it selectively blocked the growth of precancerous and cancerous HBE cells by causing cellular death, with no toxic effects on the HBE cells.
“The role of deguelin as an inhibitor of Akt activation has clinical implications, especially in the prevention and treatment of lung cancer, where controlled activation of Akt occurs at a high frequency,” said Dr. Lee. “The manipulation of Akt activity alters the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to chemotherapy and irradiation. Therefore, targeting Akt using deguelin may enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation therapy and increase the apoptotic potential of NSCLC cells.”
|