Scarlet Fever: Symptoms, Diagnosis,
Treatment and Prevention
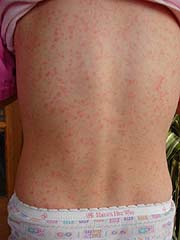
Scarlet fever is an infection caused by the streptococcus bacteria.
The bacteria cause a large number of infections including strep throat and some skin infections. The streptococcus bacteria are also responsible for certain deep tissue and bone marrow infections. When left untreated, the bacteria can cause the body to have a destructive immune reaction and cause kidney problems and heart damage.
Scarlet fever is most often caused by strep throat. The streptococcus bacteria release a toxin which irritates the skin. This causes the skin to become red with tiny bumps that feel and looks like sandpaper. Not all strains of streptococcus bacteria causes scarlet fever and not all children are sensitive to it.
Symptoms:
- Scarlet rash is the most indicative sign. The rash usually appears first on the neck and face, often leaving a clear unaffected area around the mouth. It spreads to the chest and back, then to the rest of the body. The rash usually subsides within a week, where after the skin will probably peel.
- Bright red spots on the tongue make it look like a strawberry.
- Fever of 38,3°C or higher.
- Sore throat.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Tonsils may be swollen with white or yellow spots.
- Body aches.
- Nausea.
Diagnosis:
A doctor will usually make a diagnosis based on the scarlet rash, a medical exam and by taking a throat culture.
Treatment:
Scarlet fever usually disappears within a week without any complications. The streptococcus bacteria are killed with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
Symptoms will disappear before the antibiotics are finished, however, it is imperative that the course of antibiotics is finished. The antibiotics kill the bacteria and prevent future complications.
Paracetamol or Ibuprofen will ease pain and reduce a fever.
A person with scarlet fever should drink lots of cool drinks to prevent dehydration.
Incubation Period:
This is how long it takes from being infected to showing signs and symptoms.
The incubation period for scarlet fever is 2-4 days.
Who Is At Risk?
Scarlet fever is most common in children aged 2-10, but it can affect people of any age.
Prevention:
Scarlet fever is contagious. The bacteria are spread through tiny droplets of saliva that become airborne when an infected person sneezes or coughs. Scarlet fever is sometimes spread by touching.
When a child is sick, keep him/her home for at least 5 days after starting antibiotics. Wash any eating utensils, glasses, mugs etc. separately in warm soapy water.
Possible Complications:
Complications are extremely rare, but can be serious. Possible complications include:
- Serious throat or sinus infections, which can spread to the lungs and cause pneumonia.
- Some complications like rheumatic fever and kidney damage can occur 2-3 weeks after the initial infection has passed. These extreme complications are due to a destructive immune reaction. Treatment with antibiotics dramatically reduces the changes of complications occurring.
Caring for Your Child at Home:
- Consult your doctor as soon as a child develops a rash, accompanied by fever, sore throat and/or swollen glands. Remember the streptococcus bacteria needs to be killed with antibiotics, otherwise the child could suffer complications.
- Eating could be painful, so provide soft drinks, water and a soft foods diet.
- Tea, soup, milk and ice cream could be included.
- A moist warm towel could help soothe swollen glands.
Author: Annemien van Staden
Copyright 2008: Remedium. This article may not be copied, in whole or in part, without the written consent of Remedium.
|