Symptoms and Causes of
Whooping Cough
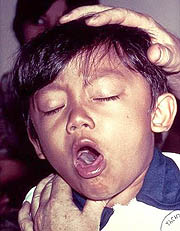
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious disease. The disease derives its name from the "whoop" sound made from the inspiration of air after a cough. Although many medical sources describe the whoop as "high-pitched", this is generally the case with infected babies and children only, not adults.
SYMPTOMS:
A week or two after exposure, the catarrhal stage begins. The eyes may be red and the child seems to have a cold in the head. There is sneezing and watering of the eyes. Then a persistent cough develops, especially bad at night. This coughing continues a week and keeps getting worse — this is the most significant indication that the problem may be whooping cough.
In about 2 weeks, the typical whoop begins. At first, only 1-2 times a day; it degrades to every time there is coughing. It is a deep breath at the end of a series of deep coughs. The child’s face may be reddish or bluish from the effort and lack of air. Vomiting may also occur. This whooping stage lasts 3-6 weeks; the cough may not entirely disappear for several months.
CAUSES:
Whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. Humans are the only known reservoir of these bacteria.
Whooping cough is spread by contact with droplets coughed out by someone with the disease or by contact with recently contaminated hard surfaces upon which the droplets landed. The bacteria thrive in the respiratory passages where they produce toxins that damage the tiny hairs (cilia) that are needed to remove particulate matter and cellular debris that are normally introduced into the airways with each breath. This results in an increased inflammation of the respiratory passages and the typical dry cough which is the hallmark of the infection.
Whooping cough is contagious from seven days after exposure to the bacteria and up to three weeks after the onset of coughing spasms. The most contagious time is during the first stage of the illness.
Initially thought to be a disease of childhood, recent studies have shown that adults are susceptible to whooping cough and account for up to 25 percent of cases. The disease, however, tends to be milder in adults and adolescents ? a persistent cough much like an upper respiratory infection or cold.
|